Dive into the fascinating world of cell division with our comprehensive Cells Alive Cell Cycle Worksheet. This interactive resource empowers you to grasp the intricacies of the cell cycle, from its stages to its regulation, providing a solid foundation for understanding cell biology and its implications in health and disease.
Throughout this engaging worksheet, you’ll embark on a journey of discovery, exploring the checkpoints that govern cell cycle progression, the role of key molecules like cyclins and CDKs, and the practical applications of cell cycle knowledge in diagnosing and treating diseases.
Introduction
The “Cells Alive Cell Cycle” worksheet is designed to enhance your understanding of the fundamental processes involved in cell division. The cell cycle is a crucial aspect of cell biology, as it governs the growth, reproduction, and repair of all living organisms.
By completing this worksheet, you will gain insights into the different stages of the cell cycle, their significance, and the factors that regulate them.
Importance of Understanding the Cell Cycle
Understanding the cell cycle is essential for several reasons. It helps us:
- Comprehend the mechanisms that drive cell growth and proliferation.
- Identify and treat diseases that arise from disruptions in the cell cycle, such as cancer.
- Develop strategies for tissue regeneration and repair.
- Gain insights into the fundamental processes of life and the functioning of living organisms.
Cell Cycle Overview
The cell cycle is a fundamental process by which cells grow and divide, ensuring the continuity of life. It is a continuous, regulated sequence of events that culminates in cell division, producing two daughter cells.
Stages of the Cell Cycle
The cell cycle consists of four distinct stages:
- G1 Phase (Gap 1):Cells grow and prepare for DNA replication.
- S Phase (Synthesis):DNA is replicated, resulting in two identical copies of each chromosome.
- G2 Phase (Gap 2):Cells continue to grow and synthesize proteins necessary for cell division.
- M Phase (Mitosis):Chromosomes condense, the nuclear envelope breaks down, and the cell divides into two daughter cells.
Cell Cycle Regulation
The cell cycle is a tightly regulated process that ensures the accurate and timely progression of cells through the various stages. Key checkpoints in the cell cycle, such as the G1/S, S, and G2/M checkpoints, act as gatekeepers, ensuring that certain conditions are met before cells proceed to the next stage.
These checkpoints monitor factors such as DNA integrity, nutrient availability, and growth signals.
Cyclins and Cyclin-Dependent Kinases (CDKs)
Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) play crucial roles in cell cycle regulation. Cyclins are proteins whose levels fluctuate throughout the cell cycle, binding to and activating CDKs. Different cyclin-CDK complexes are responsible for specific transitions within the cell cycle. For example, the cyclin D-CDK4/6 complex is involved in the G1/S transition, while the cyclin E-CDK2 complex promotes entry into S phase.
These cyclin-CDK complexes phosphorylate target proteins, including transcription factors and other regulatory proteins, to drive the cell cycle forward.
Worksheet Activities
The worksheet provides interactive exercises to reinforce your understanding of the cell cycle. These activities engage you in analyzing data, applying concepts, and practicing problem-solving.
Follow these steps to complete each activity:
Activity 1: Cell Cycle Phases Identification
- Examine the provided microscope images.
- Identify the different stages of the cell cycle (interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis) based on cellular structures and chromosome appearance.
- Complete the table by filling in the correct phase for each image.
Activity 2: Cell Cycle Data Analysis
- Analyze the data table containing cell counts at different time points.
- Calculate the duration of each cell cycle phase (G1, S, G2, M).
- Determine the growth rate of the cell population.
Activity 3: Cell Cycle Regulation Simulation
- Use the provided interactive simulation to explore the role of checkpoints and regulatory proteins in controlling the cell cycle.
- Simulate different scenarios by manipulating checkpoint activity and observe the impact on cell cycle progression.
- Draw conclusions about the importance of cell cycle regulation in maintaining genomic stability and preventing uncontrolled cell growth.
Activity 4: Case Study: Cancer and Cell Cycle Dysregulation
- Read the case study about cancer development and cell cycle dysregulation.
- Discuss how mutations in cell cycle regulatory genes can lead to uncontrolled cell division.
- Explain the potential consequences of cell cycle dysregulation in cancer progression and metastasis.
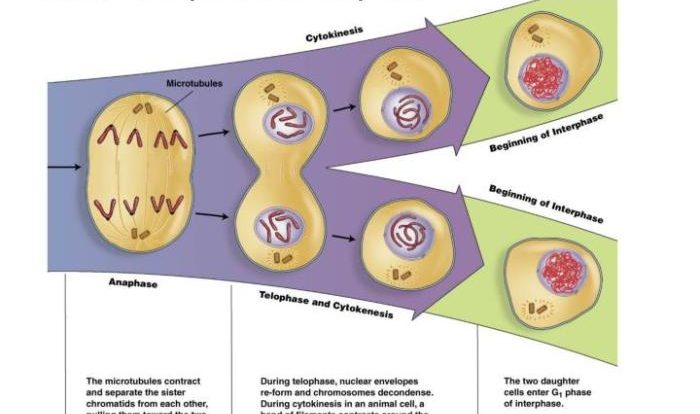
Visual Aids
Visual aids are essential for understanding the cell cycle, as they provide a clear and concise representation of the complex processes involved. Flowcharts and diagrams illustrate the sequence of events in the cell cycle, while images and animations demonstrate key cell cycle events in a dynamic and engaging way.
Flowcharts and Diagrams
Flowcharts and diagrams are useful for visualizing the cell cycle as a step-by-step process. They typically include boxes or circles representing the different stages of the cell cycle, with arrows connecting them to show the progression of events. This visual representation makes it easy to understand the order and timing of cell cycle events.
Images and Animations
Images and animations provide a more dynamic way to visualize cell cycle events. Images can capture specific moments in the cell cycle, such as the formation of chromosomes or the separation of daughter cells. Animations can show the entire cell cycle in motion, allowing viewers to see how the different stages transition into each other.
These visual aids can help to make the cell cycle more relatable and easier to understand.
Interactive Elements
Incorporating interactive elements into the cell cycle worksheet enhances student engagement and reinforces their understanding.
Here are some suggestions for interactive elements:
Quiz
Design a quiz with multiple-choice or short-answer questions that test students’ knowledge of the cell cycle stages, key checkpoints, and regulatory mechanisms.
Interactive Simulation, Cells alive cell cycle worksheet
Create an interactive simulation that allows students to explore the cell cycle in real-time. This could include features such as:
- Visualizing the different cell cycle stages
- Simulating the effects of mutations or environmental factors on the cell cycle
- Exploring the role of cell cycle checkpoints
Discussion Forum
Establish a discussion forum where students can post questions, share insights, and engage in discussions about the cell cycle. This provides a platform for peer-to-peer learning and allows students to clarify their understanding.
Conclusion: Cells Alive Cell Cycle Worksheet
Congratulations on completing the Cell Cycle Worksheet! We hope you have gained a deeper understanding of this fundamental process in cell biology.
The cell cycle is a complex and tightly regulated process that ensures the proper growth, development, and reproduction of all living organisms. Understanding the cell cycle is essential for comprehending various biological phenomena, including cell division, tissue repair, and cancer development.
Call to Action
We encourage you to continue exploring the topic of the cell cycle. There are numerous resources available online and in libraries that can provide you with additional information and insights.
By delving deeper into the cell cycle, you will not only expand your knowledge of cell biology but also gain a greater appreciation for the intricate mechanisms that govern life itself.
Query Resolution
What is the purpose of the Cells Alive Cell Cycle Worksheet?
The Cells Alive Cell Cycle Worksheet is designed to provide a comprehensive understanding of the cell cycle, its stages, regulation, and practical applications.
What are the key stages of the cell cycle?
The cell cycle consists of four main stages: G1, S, G2, and M (mitosis or meiosis).
How is the cell cycle regulated?
The cell cycle is tightly regulated by checkpoints and key molecules like cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs).