Spanish speaking countries and their capitals word search – Embark on a captivating journey into the realm of Spanish-speaking countries and their capitals with this comprehensive guide. As we delve into the rich history, cultural tapestry, and economic ties that bind these nations together, prepare to be enlightened by an in-depth analysis and interactive resources that bring this fascinating topic to life.
This meticulously crafted guide will equip you with an unparalleled understanding of the Spanish-speaking world, fostering a deeper appreciation for its diverse cultures and the profound impact of Spanish colonialism.
Spanish-Speaking Countries and Their Capitals: Spanish Speaking Countries And Their Capitals Word Search
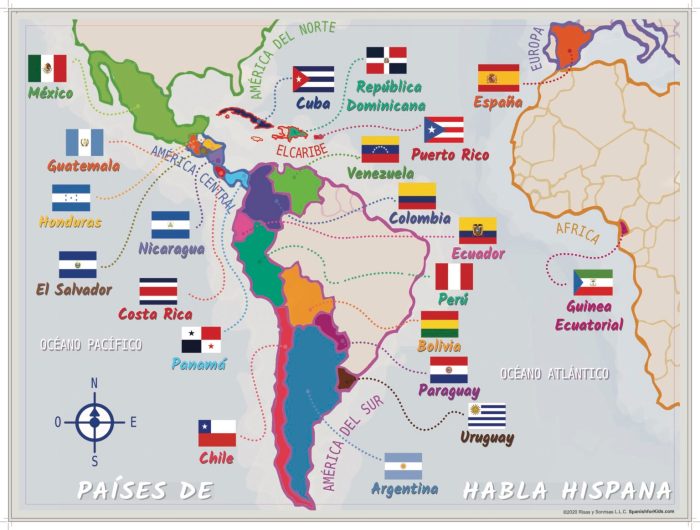
The Spanish language, with its rich history and global reach, is spoken by over 500 million people across the world. Spanish-speaking countries, also known as the Hispanic world, encompass a diverse array of nations, each with its unique cultural heritage and political landscape.
The following table provides a comprehensive list of Spanish-speaking countries and their respective capital cities, along with the population of each capital as of 2023:
| Country | Capital | Population |
|---|---|---|
| Argentina | Buenos Aires | 3,114,000 |
| Bolivia | Sucre | 316,900 |
| Chile | Santiago | 6,315,000 |
| Colombia | Bogotá | 11,030,000 |
| Costa Rica | San José | 1,000,000 |
| Cuba | Havana | 2,160,000 |
| Dominican Republic | Santo Domingo | 3,690,000 |
| Ecuador | Quito | 2,792,000 |
| El Salvador | San Salvador | 2,221,000 |
| Equatorial Guinea | Malabo | 118,300 |
| Guatemala | Guatemala City | 1,215,000 |
| Honduras | Tegucigalpa | 1,123,000 |
| Mexico | Mexico City | 21,581,000 |
| Nicaragua | Managua | 1,640,000 |
| Panama | Panama City | 1,619,000 |
| Paraguay | Asunción | 524,000 |
| Peru | Lima | 10,478,000 |
| Puerto Rico | San Juan | 395,300 |
| Spain | Madrid | 6,755,000 |
| Uruguay | Montevideo | 1,414,000 |
| Venezuela | Caracas | 3,234,000 |
Historical Significance of Spanish Colonialism
Spanish colonialism played a pivotal role in shaping the development of Spanish-speaking countries. Beginning in the 15th century, Spain established a vast empire that spanned across the Americas, Africa, and Asia.
The Spanish conquistadors brought with them their language, culture, and religion, which had a profound impact on the indigenous populations of the colonized territories. Spanish became the official language of many of these countries, and Catholicism became the dominant religion.
Spanish colonialism also had a significant economic impact on the Americas. The Spanish introduced new crops, such as sugar and coffee, which became major export commodities. The exploitation of natural resources, such as gold and silver, also played a key role in the Spanish economy.
The legacy of Spanish colonialism is still evident in many Spanish-speaking countries today. The Spanish language, culture, and religion continue to play a major role in the lives of the people of these countries.
Economic and Cultural Ties

Spanish-speaking countries share strong economic and cultural ties. Trade, tourism, and cultural exchange play a key role in fostering these ties.
The Spanish-speaking world is a major economic bloc, with a combined GDP of over $5 trillion. The countries of the region trade extensively with each other, and they are also major exporters to the United States and Europe.
Tourism is another important industry for Spanish-speaking countries. The region is home to some of the world’s most popular tourist destinations, such as Mexico City, Machu Picchu, and the Galapagos Islands.
Cultural exchange is also a key part of the relationship between Spanish-speaking countries. The region has a rich cultural heritage, which is shared through music, art, literature, and film.
Challenges and Opportunities
Spanish-speaking countries face a number of challenges in the 21st century, including poverty, inequality, and political instability.
Poverty is a major problem in many Spanish-speaking countries. According to the World Bank, over 100 million people in the region live in extreme poverty.
Inequality is also a major challenge. The gap between the rich and the poor is growing in many Spanish-speaking countries.
Political instability is another challenge. Many Spanish-speaking countries have experienced political instability in recent years, which has led to violence and economic disruption.
Despite these challenges, Spanish-speaking countries also have a number of opportunities for growth and development. The region has a young and growing population, and it is home to a number of natural resources.
Education, technology, and infrastructure are key areas for investment in Spanish-speaking countries. By investing in these areas, these countries can improve their economic prospects and reduce poverty and inequality.
FAQ Explained
What are the most populous capital cities in the Spanish-speaking world?
Mexico City, Buenos Aires, Madrid, Bogotá, and Lima rank among the most populous capital cities in the Spanish-speaking world.
How has Spanish colonialism influenced the cultures of Spanish-speaking countries?
Spanish colonialism has left an indelible mark on the cultures of Spanish-speaking countries, shaping their languages, religions, traditions, and political systems.
What are some key economic sectors that foster collaboration among Spanish-speaking countries?
Tourism, trade, and agriculture are among the key economic sectors that foster collaboration and interdependence among Spanish-speaking countries.