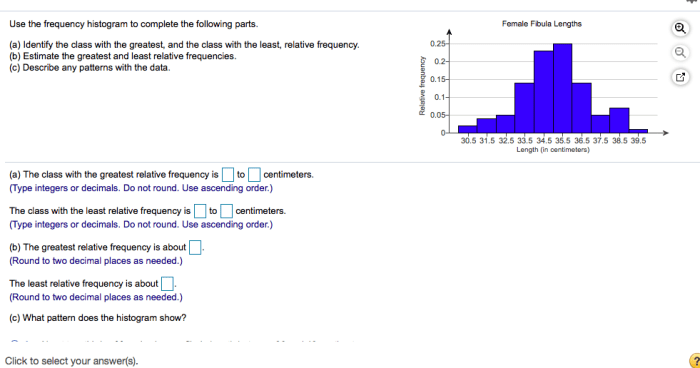
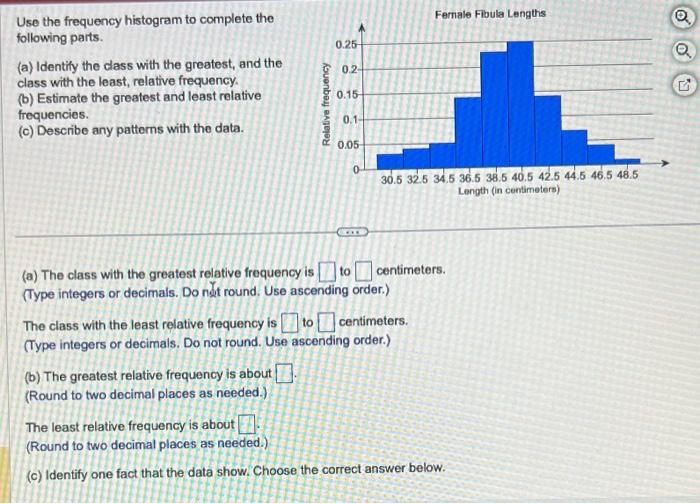
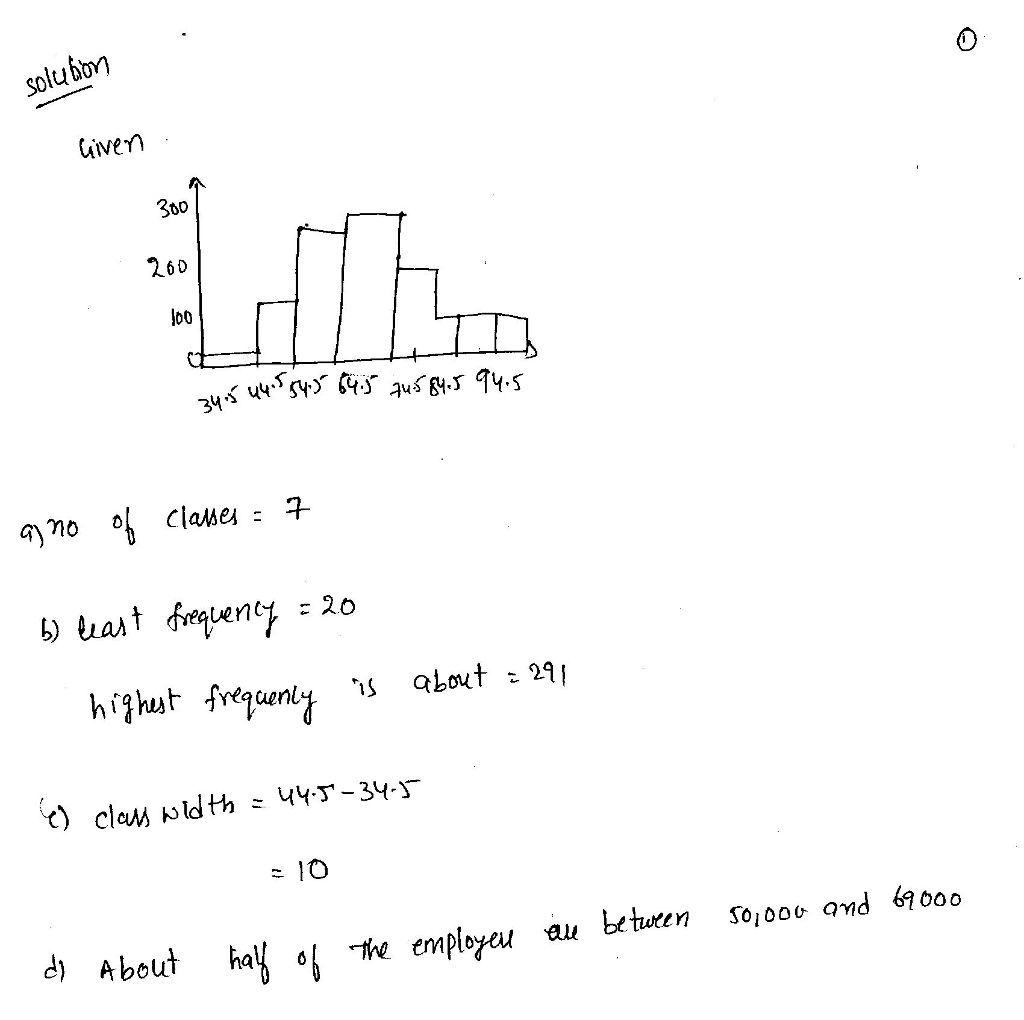Use the frequency histogram to complete the following parts. – Welcome to the definitive guide on using frequency histograms, a powerful data visualization technique that unveils the distribution patterns within your datasets. Embark on a journey of discovery as we delve into the intricacies of frequency histograms, empowering you to make informed decisions and gain actionable insights from your data.
Frequency histograms stand as a cornerstone of data analysis, providing a visual representation of the frequency of occurrence for different values within a dataset. This versatile tool finds applications across diverse fields, from finance and healthcare to manufacturing and social sciences.
Its simplicity and effectiveness make it an indispensable asset for data-driven decision-making.
Frequency Histogram
A frequency histogram is a graphical representation of the distribution of data. It displays the frequency of occurrence of different values or ranges of values in a dataset. The x-axis of a frequency histogram represents the values or ranges, while the y-axis represents the frequency of occurrence.
Frequency histograms are useful for visualizing the distribution of data and identifying patterns and trends. They can be used to compare different datasets, identify outliers, and make inferences about the underlying population.
Histogram Analysis
The elements of a frequency histogram include the bins, the frequency axis, and the x-axis. The bins are the intervals or ranges of values that are represented on the x-axis. The frequency axis shows the number of observations that fall within each bin.
The x-axis shows the values or ranges of values that are being represented.
The shape and spread of a frequency histogram can provide insights into the distribution of data. A symmetrical histogram indicates that the data is normally distributed. A skewed histogram indicates that the data is not normally distributed. The spread of the histogram indicates the variability of the data.
Histogram Applications, Use the frequency histogram to complete the following parts.
Frequency histograms are used in various fields, including statistics, data analysis, and quality control. They are used to visualize the distribution of data, identify patterns and trends, and make inferences about the underlying population.
Benefits of using frequency histograms include their simplicity, ease of interpretation, and ability to identify patterns and trends. Limitations of using frequency histograms include their sensitivity to the choice of bin size and their inability to show the relationship between variables.
Advanced Histogram Techniques
Advanced histogram techniques include smoothing and normalizing histograms. Smoothing histograms can help to reduce noise and make patterns and trends more visible. Normalizing histograms can help to compare histograms with different bin sizes.
Advanced histogram techniques are used in a variety of applications, including image processing, signal processing, and data analysis.
HTML Table Integration
An HTML table can be used to display the frequency distribution of a dataset. The table should have two columns, one for the values or ranges of values and one for the frequency of occurrence.
The table should be designed with responsive columns for optimal viewing on different devices. The table should also include a caption and labels for the columns.
Bullet Point Examples
- Steps involved in constructing a frequency histogram:
- Divide the data into equal-width bins.
- Count the number of observations that fall within each bin.
- Plot the frequency of occurrence on the y-axis and the values or ranges of values on the x-axis.
- Key features of a frequency histogram:
- The shape of the histogram indicates the distribution of the data.
- The spread of the histogram indicates the variability of the data.
- The bins of the histogram represent the intervals or ranges of values that are being represented.
- Examples where frequency histograms are commonly used:
- To visualize the distribution of test scores in a classroom.
- To identify patterns and trends in sales data.
- To compare the distribution of data from different populations.
Key Questions Answered: Use The Frequency Histogram To Complete The Following Parts.
What are the key elements of a frequency histogram?
A frequency histogram comprises several key elements, including the x-axis representing the data values, the y-axis representing the frequency of occurrence, bins that group data into intervals, and bars that depict the frequency within each bin.
How do I interpret the shape of a frequency histogram?
The shape of a frequency histogram provides valuable insights into the distribution of data. A bell-shaped curve indicates a normal distribution, while skewed distributions suggest asymmetry. Bimodal or multimodal distributions reveal multiple peaks, indicating the presence of distinct data clusters.
What are the advantages of using frequency histograms?
Frequency histograms offer numerous advantages, including their ability to visually represent large datasets, identify patterns and trends, compare different distributions, and make inferences about the underlying population.