Articles of confederation vs constitution venn diagram – Articles of Confederation vs. Constitution Venn Diagram: A Comparative Analysis delves into the historical context, structure, powers, rights, amendment process, ratification, and historical impact of these foundational American documents. This comprehensive comparison illuminates the similarities and differences between these two pivotal texts, offering a deeper understanding of their role in shaping the United States.
The Articles of Confederation, adopted in 1781, established a loose confederation of sovereign states with limited federal authority. The Constitution, ratified in 1788, created a stronger national government with expanded powers and a system of checks and balances.
Historical Context
The Articles of Confederation were adopted in 1781, creating a loose alliance of sovereign states with limited federal authority. The weaknesses of the Articles led to the Constitutional Convention in 1787, which drafted the Constitution, ratified in 1788, establishing a stronger central government.
Structure and Organization
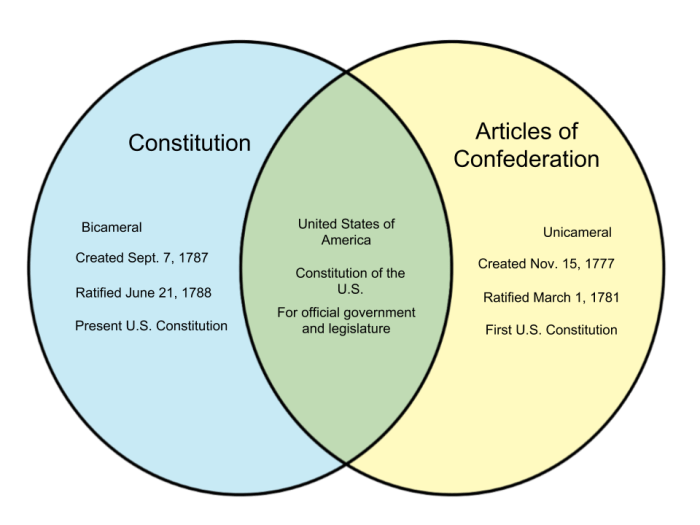
Articles of Confederation
- 13 articles, each requiring unanimous approval for amendment
- Loose confederation of states, with each state retaining sovereignty
- Weak central government with limited powers
Constitution, Articles of confederation vs constitution venn diagram
- 7 articles, with amendments requiring a two-thirds majority vote
- Stronger central government with enumerated powers
- Three branches of government: legislative, executive, and judicial
Powers of the Federal Government: Articles Of Confederation Vs Constitution Venn Diagram
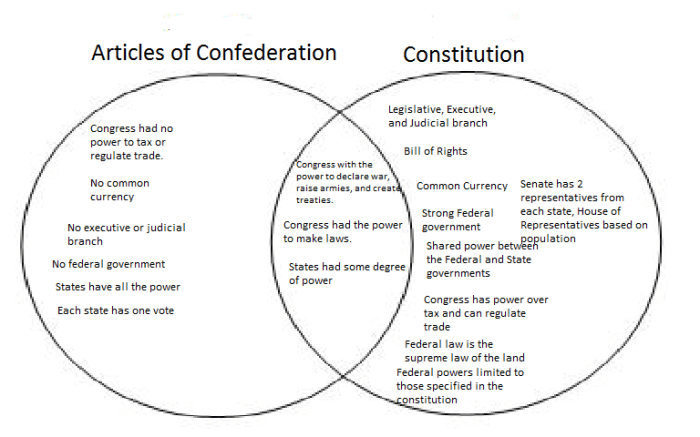
Articles of Confederation
- Declare war, make peace, and enter into treaties
- Borrow money and issue currency
- Establish a postal service
Constitution, Articles of confederation vs constitution venn diagram
- All powers granted under the Articles, plus:
- Regulate interstate commerce
- Raise and maintain an army and navy
- Establish courts
Rights of Individuals
Articles of Confederation
- No explicit protection of individual rights
Constitution, Articles of confederation vs constitution venn diagram
- Bill of Rights (first 10 amendments) guarantees:
- Freedom of speech, religion, and the press
- Right to bear arms
- Due process of law
Amendment Process

Articles of Confederation
- Unanimous approval of all states required
Constitution, Articles of confederation vs constitution venn diagram
- Two-thirds majority vote of both houses of Congress
- Ratification by three-fourths of the states
Ratification and Implementation
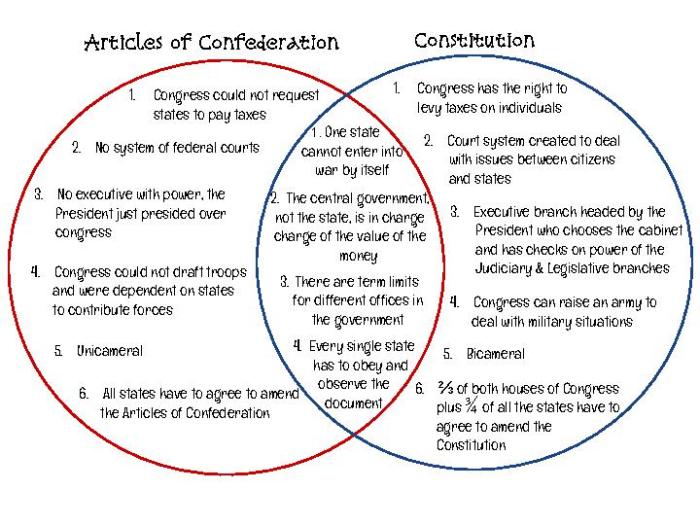
Articles of Confederation
- Ratified by all 13 states in 1781
Constitution, Articles of confederation vs constitution venn diagram
- Ratified by 9 states in 1788
- Went into effect in 1789
Helpful Answers
What were the key differences between the Articles of Confederation and the Constitution?
The Constitution granted the federal government significantly more powers than the Articles of Confederation, including the power to tax, regulate commerce, and raise an army. The Constitution also established a system of checks and balances to prevent any one branch of government from becoming too powerful.
How did the ratification process differ for the Articles of Confederation and the Constitution?
The Articles of Confederation required unanimous ratification by all 13 states, while the Constitution required ratification by only nine states.
What were the major strengths and weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation?
The Articles of Confederation’s primary strength was its emphasis on state sovereignty. However, its weakness was its inability to create a strong central government capable of addressing national issues.