Embark on an exploration of Essentials of Communication Sciences and Disorders, a field that delves into the multifaceted nature of human communication. This comprehensive guide unveils the complexities of speech, language, hearing, and swallowing, illuminating their profound impact on individuals and society.
Within this realm, professionals collaborate seamlessly, drawing upon interdisciplinary expertise to assess, diagnose, and treat communication disorders. Their unwavering commitment to ethical practices ensures the well-being and dignity of those they serve.
1. Defining Communication Sciences and Disorders

Communication sciences and disorders (CSD) is a multidisciplinary field that studies human communication and its disorders. CSD professionals are concerned with the prevention, assessment, diagnosis, and treatment of speech, language, hearing, and swallowing disorders.
CSD professionals work in a variety of settings, including schools, hospitals, clinics, and private practice. They may work with individuals of all ages, from infants to the elderly.
Common communication disorders include speech disorders (e.g., stuttering, articulation disorders), language disorders (e.g., aphasia, dyslexia), hearing disorders (e.g., hearing loss, tinnitus), and swallowing disorders (e.g., dysphagia).
These disorders can have a significant impact on an individual’s ability to communicate, participate in social activities, and learn.
2. Core Components of CSD

The key areas of study within CSD include:
- Speech: The production of spoken language, including the articulation of sounds, the use of prosody, and the sequencing of words.
- Language: The comprehension and production of spoken and written language, including the use of grammar, vocabulary, and semantics.
- Hearing: The ability to perceive and interpret sound, including the detection of speech, the localization of sound sources, and the discrimination of different sounds.
- Swallowing: The process of moving food and liquid from the mouth to the stomach, including the coordination of the muscles of the mouth, throat, and esophagus.
These areas are closely related and contribute to overall communication. For example, speech disorders can affect language development, and hearing loss can affect speech production.
Interdisciplinary collaboration is essential in CSD. CSD professionals often work with other professionals, such as physicians, occupational therapists, and psychologists, to provide comprehensive care to individuals with communication disorders.
3. Assessment and Diagnosis in CSD
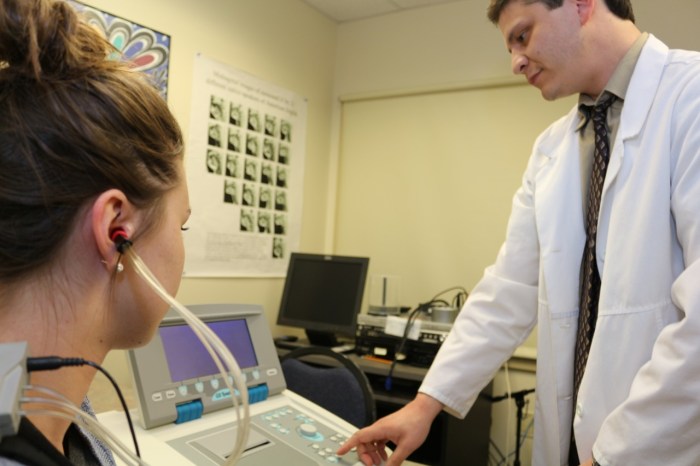
The assessment of communication disorders involves a variety of methods, including:
- Case history: A detailed interview with the individual and their family members to gather information about the individual’s communication abilities and any relevant medical or developmental history.
- Observation: Watching the individual communicate in different situations to observe their speech, language, hearing, and swallowing abilities.
- Standardized tests: Administering standardized tests to measure the individual’s communication abilities in specific areas.
Accurate diagnosis is essential for developing effective treatment plans. CSD professionals use a variety of diagnostic criteria to determine the specific type of communication disorder that an individual has.
Specific assessment tools include:
- Speech-Language Evaluation Protocol (SLEP): A comprehensive assessment tool that measures speech and language abilities in children and adults.
- Peabody Picture Vocabulary Test (PPVT): A standardized test that measures vocabulary development in children and adults.
- Pure-Tone Audiometry: A test that measures hearing sensitivity at different frequencies.
Top FAQs: Essentials Of Communication Sciences And Disorders
What are the common communication disorders?
Communication disorders encompass a wide range, including speech disorders (e.g., stuttering, apraxia), language disorders (e.g., aphasia, dyslexia), hearing disorders (e.g., hearing loss, tinnitus), and swallowing disorders (e.g., dysphagia).
How are communication disorders diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a thorough assessment by a qualified professional, utilizing standardized tests, observation, and medical imaging techniques to identify the specific communication disorder and its underlying causes.
What are the treatment options for communication disorders?
Treatment plans are tailored to the individual’s needs and may include speech therapy, language therapy, auditory training, or a combination of approaches. These therapies aim to improve communication skills, reduce symptoms, and enhance overall quality of life.
