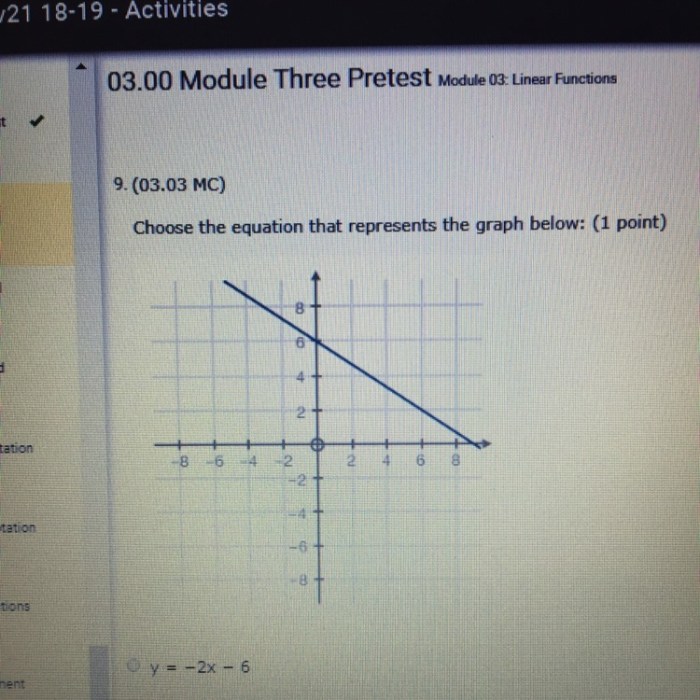
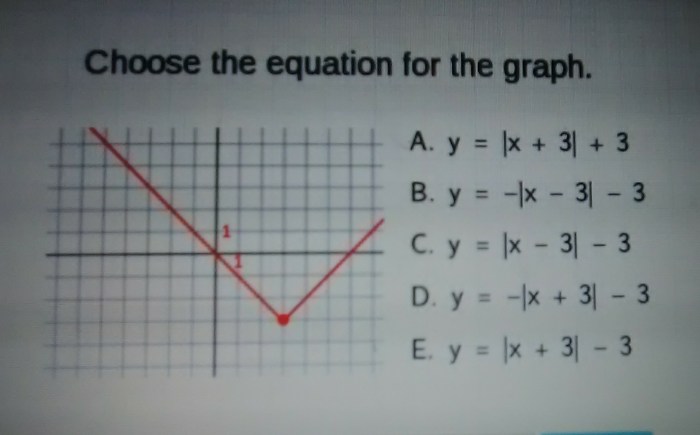
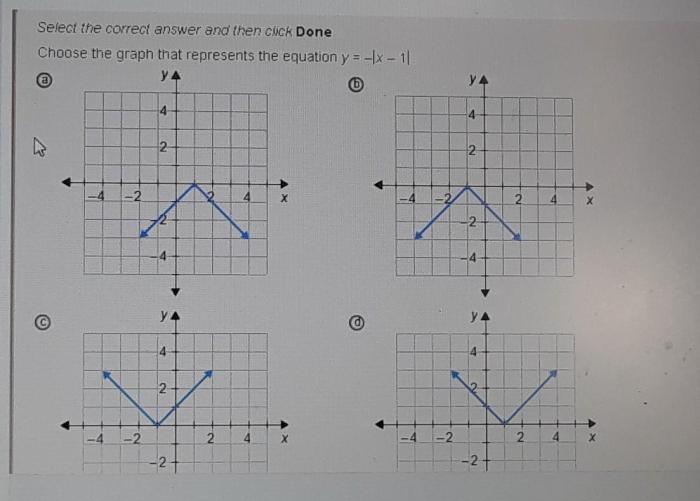
Choose the equation that represents the graph – Choosing the Equation that Represents the Graph embarks on an illuminating journey into the realm of mathematical representation, guiding readers through the intricacies of translating graphical data into precise equations. This comprehensive guide unveils the fundamental principles of linear equations, graph interpretation, and equation representation, empowering readers with the tools to navigate the complex world of data analysis.
Delving into the nuances of linear equations, we explore their graphical manifestations, unraveling the relationship between slope and y-intercept and their impact on graph behavior. Through a series of carefully crafted examples, we illustrate the process of discerning key graph features, determining domain and range, and identifying intercepts, laying the groundwork for accurate graph analysis.
Equation Analysis: Choose The Equation That Represents The Graph
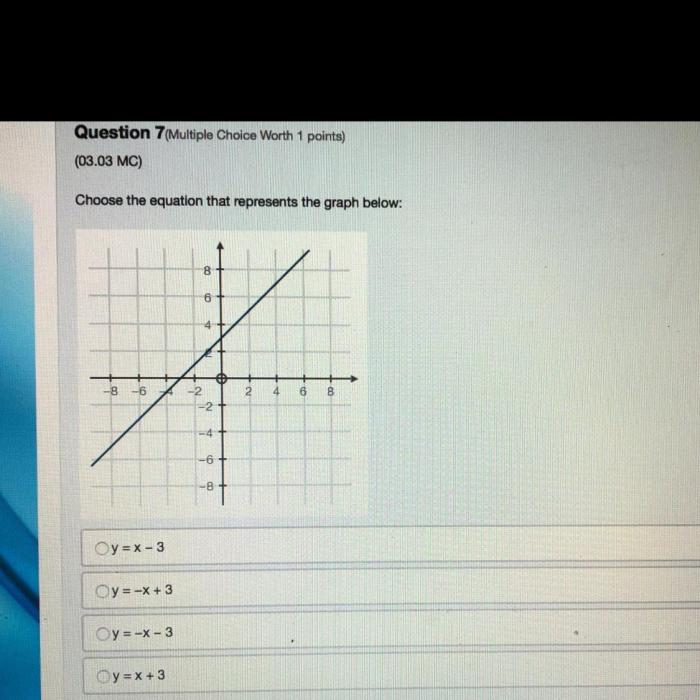
Linear equations represent a fundamental concept in mathematics and have numerous applications in various fields. They are defined as equations of the form y = mx + b, where m represents the slope and b represents the y-intercept of the line.
The graphical representation of a linear equation is a straight line. The slope determines the steepness of the line, while the y-intercept represents the point where the line intersects the y-axis.
Graph Interpretation
When analyzing a graph, it is essential to identify its key features. The x-axis represents the independent variable, while the y-axis represents the dependent variable. The origin (0, 0) is the point where the x-axis and y-axis intersect.
The domain of a function refers to the set of all possible input values (x-values), while the range refers to the set of all possible output values (y-values).
Intercepts are points where the graph intersects the x-axis or y-axis. The x-intercept represents the value of x when y is 0, while the y-intercept represents the value of y when x is 0.
Equation Representation
To write an equation that represents a given graph, determine the slope and y-intercept of the line.
The slope can be calculated using the formula m = (y2 – y1) / (x2 – x1), where (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) are two points on the line.
The y-intercept can be found by substituting any point on the line into the equation y = mx + b and solving for b.
Once the slope and y-intercept are known, the equation of the line can be written in slope-intercept form: y = mx + b.
Graphing Techniques, Choose the equation that represents the graph
Various techniques can be used to graph equations. Point-plotting involves plotting points on the graph and connecting them with a line.
Slope-intercept form is a convenient method for graphing linear equations. By plotting the y-intercept on the y-axis and using the slope to determine the direction of the line, the graph can be constructed.
Transformations, such as translations and rotations, can be applied to graphs to create new graphs that represent related functions.
Applications
Choosing the correct equation to represent a graph is crucial in various real-world applications. In science, graphs are used to represent data and derive relationships between variables.
In engineering, graphs are used to design and analyze systems. In economics, graphs are used to model supply and demand.
Selecting the appropriate equation ensures accurate data analysis and effective problem-solving in these and other fields.
Detailed FAQs
What is the significance of choosing the correct equation to represent a graph?
Choosing the correct equation is crucial for accurate data analysis and problem-solving. It ensures that the equation faithfully captures the behavior of the graph, enabling reliable predictions and inferences.
How can I determine the slope of a line from its graph?
To determine the slope, identify two points on the line and calculate the change in y (rise) divided by the change in x (run). The resulting value represents the slope.
What is the relationship between the slope and y-intercept of a linear equation?
The slope determines the steepness of the line, while the y-intercept represents the point where the line crosses the y-axis. Together, they uniquely define the linear equation.