Chapter 4 tissue the living fabric – Embarking on Chapter 4: Tissues: The Living Fabric, we delve into the intricate world of tissues, the fundamental building blocks of life. This exploration unveils the diverse array of tissues that orchestrate the intricate functions of living organisms.
Tissues, the organizational units of cells, play a pivotal role in shaping the structure and function of all living organisms. From the protective barriers of epithelial tissues to the contractile power of muscle tissues, tissues are the embodiment of life’s complexity and adaptability.
Cellular Basis of Life
Cells are the fundamental units of life. They are the smallest units that can carry out all the functions of life, including metabolism, growth, reproduction, and response to stimuli. Cells are highly organized and specialized, and they work together to form tissues and organs.There
are two main types of cells: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells are smaller and simpler than eukaryotic cells, and they do not have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells are larger and more complex, and they have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.The
cell theory is a fundamental principle of biology that states that all living things are composed of cells, that all cells arise from pre-existing cells, and that the activity of an organism is the sum of the activities of its individual cells.
The cell theory is one of the most important and well-supported theories in biology.
Tissues: The Living Fabric: Chapter 4 Tissue The Living Fabric
Tissues are groups of cells that have similar structure and function. Tissues are organized into organs, which are groups of tissues that work together to perform a specific function. There are four primary types of tissues: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous.Epithelial
tissue covers the surfaces of the body and lines the cavities of the body. It protects the body from the environment and helps to regulate the passage of materials into and out of the body.Connective tissue supports and connects the other tissues of the body.
It also stores fat and provides insulation.Muscle tissue allows the body to move. There are three types of muscle tissue: skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle.Nervous tissue transmits information throughout the body. It is composed of neurons, which are specialized cells that transmit electrical signals, and glial cells, which support and protect the neurons.
Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial tissue is composed of cells that are closely packed together and form a continuous layer. The cells are usually thin and flat, and they have a variety of specialized functions.There are many different types of epithelial tissue, each with its own unique structure and function.
Some of the most common types of epithelial tissue include:*
- *Simple squamous epithelium is composed of a single layer of thin, flat cells. It is found in the lining of the blood vessels and the alveoli of the lungs.
- *Simple cuboidal epithelium is composed of a single layer of cube-shaped cells. It is found in the lining of the kidneys and the ducts of the glands.
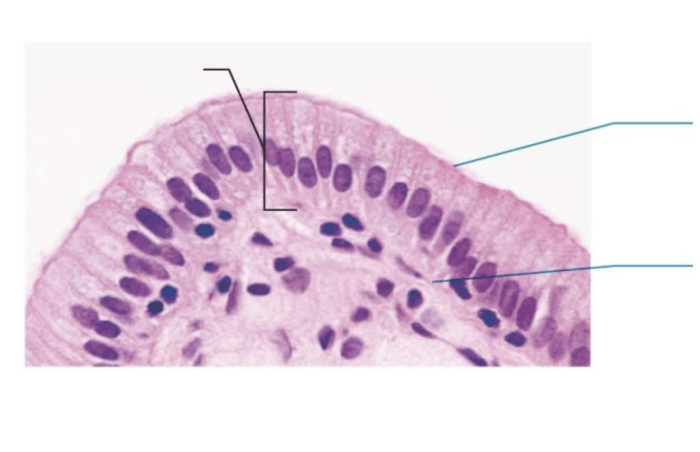
- *Simple columnar epithelium is composed of a single layer of tall, column-shaped cells. It is found in the lining of the digestive tract and the respiratory tract.
- *Stratified squamous epithelium is composed of multiple layers of cells. The cells in the outermost layer are flat, while the cells in the innermost layer are cuboidal or columnar. It is found in the lining of the skin and the esophagus.
Connective Tissue
Connective tissue is the most abundant type of tissue in the body. It supports and connects the other tissues of the body, and it also stores fat and provides insulation.There are many different types of connective tissue, each with its own unique structure and function.
Some of the most common types of connective tissue include:*
- *Loose connective tissue is composed of cells that are loosely arranged in a matrix of collagen fibers. It is found in the subcutaneous layer of the skin and around the blood vessels and nerves.
- *Dense connective tissue is composed of cells that are closely packed together in a matrix of collagen fibers. It is found in the tendons and ligaments.
- *Cartilage is a specialized type of connective tissue that is composed of cells that are embedded in a matrix of collagen and other proteins. It is found in the joints, the ears, and the nose.
- *Bone is a specialized type of connective tissue that is composed of cells that are embedded in a matrix of calcium and other minerals. It is found in the skeleton.
Muscle Tissue
Muscle tissue allows the body to move. There are three types of muscle tissue: skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle.*
- *Skeletal muscle is attached to the bones and is responsible for voluntary movement. It is composed of long, cylindrical cells that are multinucleated.
- *Smooth muscle is found in the walls of the blood vessels and the digestive tract. It is composed of spindle-shaped cells that are uninucleated.
- *Cardiac muscle is found in the heart. It is composed of branched cells that are interconnected by intercalated discs.
Nervous Tissue

Nervous tissue transmits information throughout the body. It is composed of neurons, which are specialized cells that transmit electrical signals, and glial cells, which support and protect the neurons.Neurons have a cell body, which contains the nucleus, and several extensions called dendrites and axons.
Dendrites receive signals from other neurons, while axons transmit signals to other neurons.Glial cells are the most abundant type of cell in the nervous system. They support and protect the neurons, and they also help to maintain the homeostasis of the nervous system.
Clarifying Questions
What are the four primary types of tissues?
Epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissues.
What is the function of connective tissue?
To provide support, protection, and connection between cells and organs.
How do muscle tissues contribute to movement?
By contracting and relaxing, generating force that enables movement.